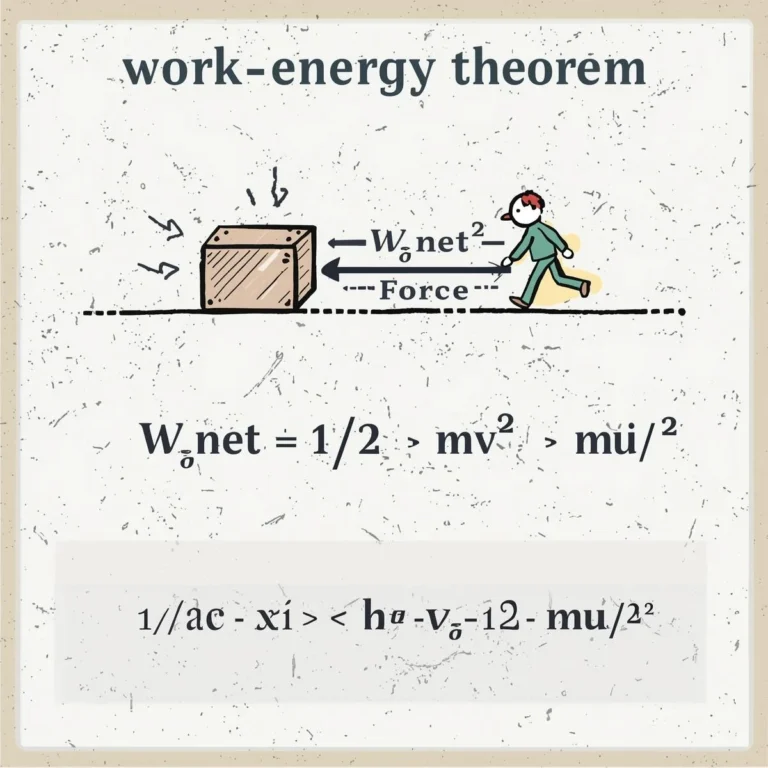
Definition
Equilibrium of forces refers to the condition in which the vector sum of all the forces acting on a body is zero, resulting in no change in the state of rest or uniform motion of the body. In this state, the body is said to be in equilibrium.
Types of Equilibrium
- Static Equilibrium:
The body remains at rest under the action of forces. - Dynamic Equilibrium:
The body moves with constant velocity under the action of forces.
Conditions for Equilibrium
- Translational Equilibrium:
The sum of all forces acting on the body is zero.
Formula:
ΣF = 0 - Rotational Equilibrium:
The sum of all torques acting on the body is zero.
Formula:
Στ = 0
Example
A book resting on a table is in static equilibrium. The gravitational force (weight) acting downward is balanced by the normal reaction force from the table acting upward, so the net force is zero.
Illustrative Image
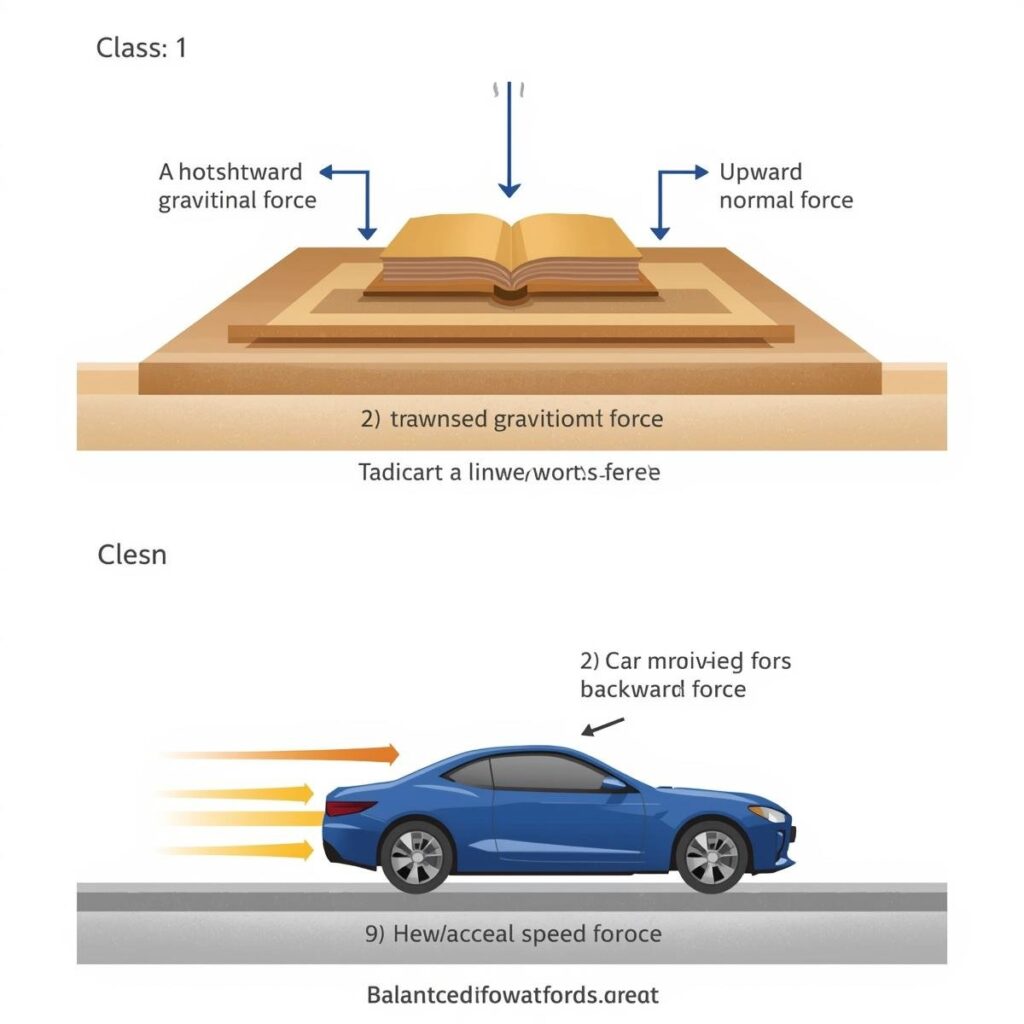
Summary Table
| Type | Condition | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Static | Body at rest | ΣF = 0 | Book on table |
| Dynamic | Body in uniform motion | ΣF = 0 | Car moving at constant speed |