Definition
In mechanics, forces are interactions that can change the state of motion of objects. Common forces are those frequently encountered in everyday situations and basic physics problems.
Types of Common Forces
1. Gravitational Force
Definition:
The force of attraction between any two objects with mass.
Formula:
F = mg
Where:
- F = gravitational force (N)
- m = mass of the object (kg)
- g = acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s²)
Example:
A ball falling towards the ground experiences gravitational force.
2. Normal Force
Definition:
The perpendicular contact force exerted by a surface on an object resting on it.
Formula:
For a horizontal surface:
N = mg
Example:
A book resting on a table experiences an upward normal force from the table.
3. Tension Force
Definition:
The pulling force transmitted through a string, rope, or cable when it is pulled tight by forces acting from opposite ends.
Formula:
If the object is hanging and at rest:
T = mg
Example:
A hanging lamp suspended by a cable experiences tension in the cable.
4. Frictional Force
Definition:
The force that opposes the relative motion or tendency of such motion of two surfaces in contact.
Formula:
f = μN
Where:
- f = frictional force (N)
- μ = coefficient of friction
- N = normal force (N)
Example:
A box sliding on the floor experiences frictional force opposing its motion.
5. Applied Force
Definition:
A force that is applied to an object by a person or another object.
Example:
Pushing a shopping cart involves an applied force.
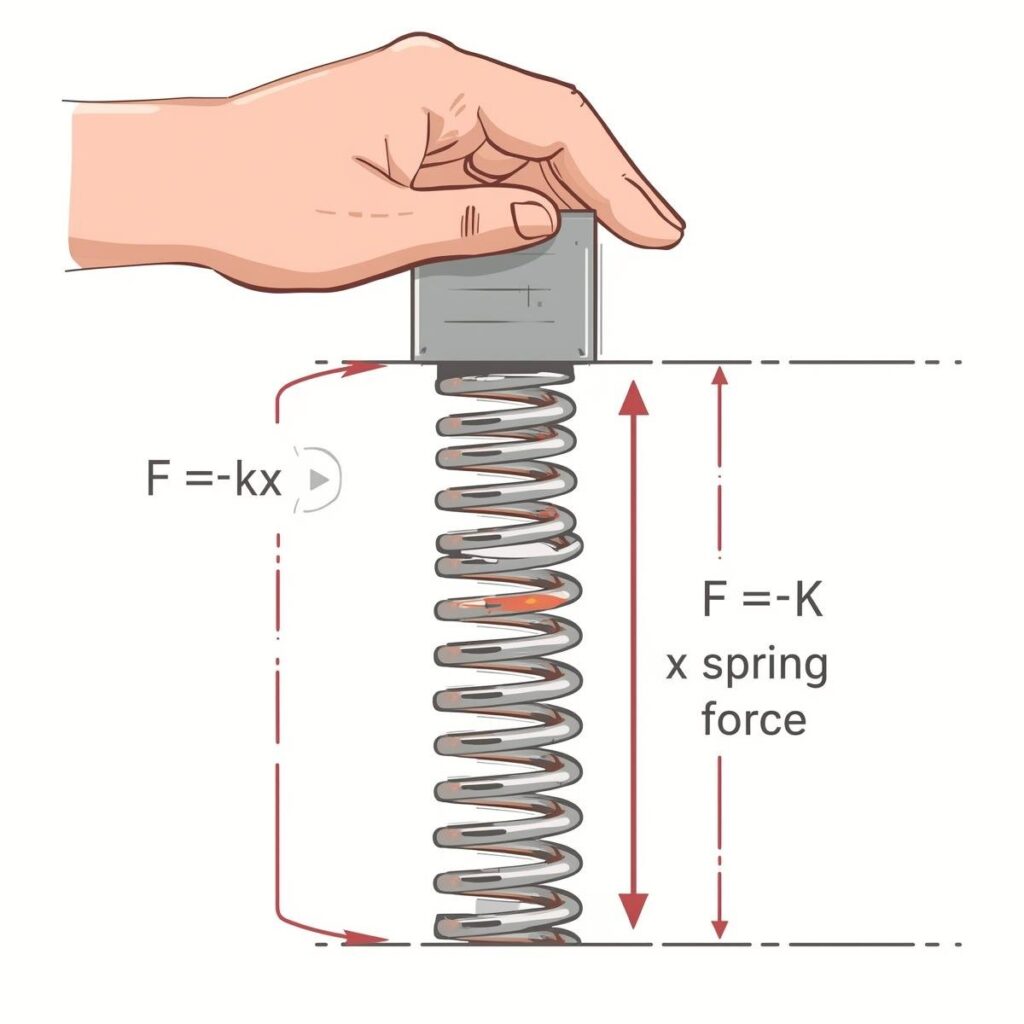
6. Spring Force
Definition:
The force exerted by a compressed or stretched spring upon any object that is attached to it.
Formula:
F = -kx
Where:
- F = spring force (N)
- k = spring constant (N/m)
- x = displacement from equilibrium (m)
Example:
A mass attached to a stretched spring experiences a restoring spring force.
Illustrative Image
Summary Table
| Force | Definition | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gravitational | Attraction between masses | F = mg | Ball falling down |
| Normal | Perpendicular contact force | N = mg | Book on table |
| Tension | Force in string/rope | T = mg | Hanging lamp |
| Friction | Opposes motion | f = μN | Box sliding |
| Applied | External push or pull | — | Pushing cart |
| Spring | Restoring force in spring | F = -kx | Stretched spring |


I am not very wonderful with English but I get hold this rattling easy to translate.