Definition
Energy is the capacity to do work. It exists in various forms and can be transformed from one form to another, but cannot be created or destroyed.
Formula
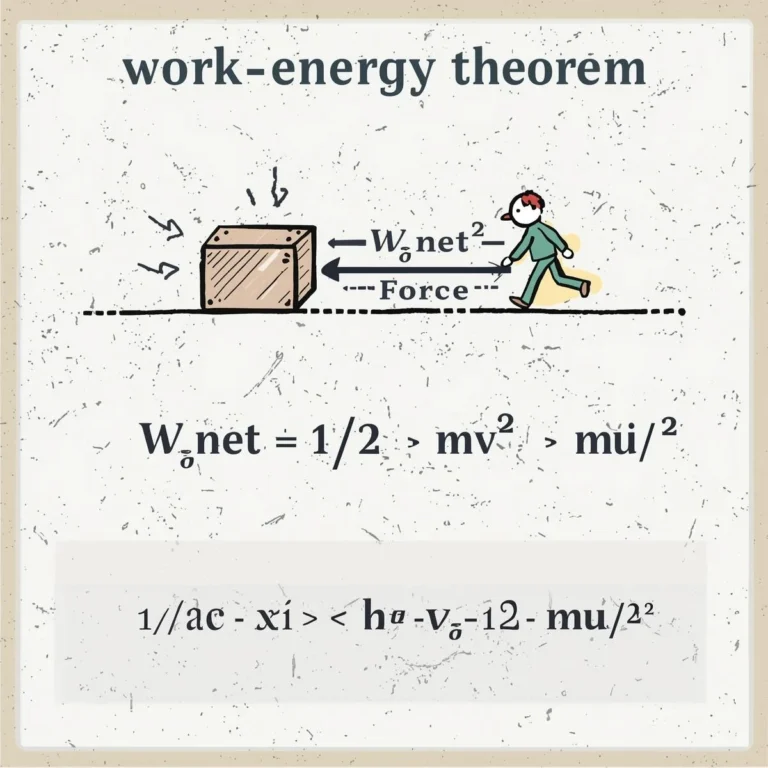
- Work-Energy Principle:
W = ΔE
(Work done on an object is equal to the change in its energy.) - Kinetic Energy (KE):
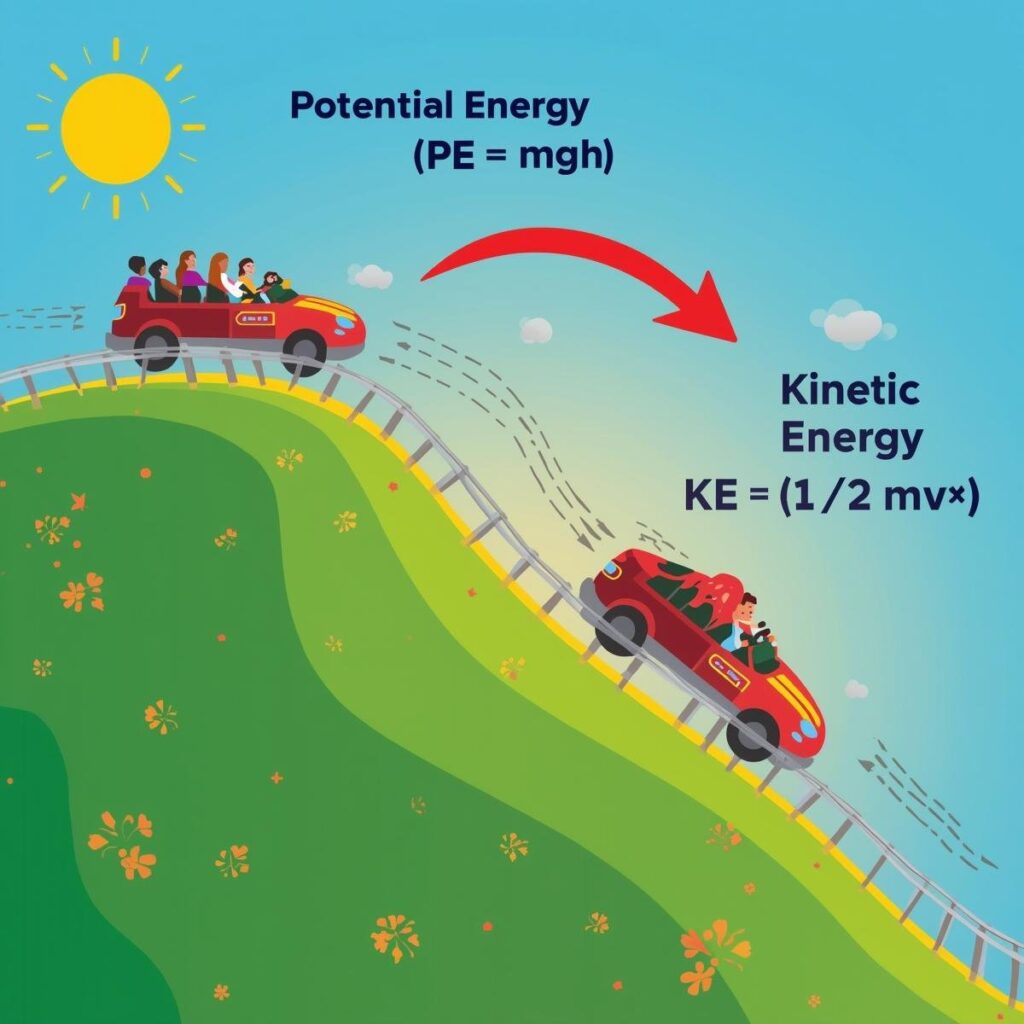
KE = (1/2)mv²
Where:
m = mass (kg)
v = velocity (m/s) - Potential Energy (PE):
PE = mgh
Where:
m = mass (kg)
g = acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s²)
h = height (m)
Example
- Kinetic Energy Example:
A car of mass 1000 kg moving at 20 m/s:
KE = (1/2) × 1000 × (20)² = 200,000 J - Potential Energy Example:
A stone of mass 2 kg at a height of 5 m:
PE = 2 × 9.8 × 5 = 98 J
Types of Energy
- Kinetic Energy: Energy due to motion.
- Potential Energy: Energy due to position or configuration.
- Mechanical Energy: Sum of kinetic and potential energy.
- Chemical Energy: Stored in chemical bonds.
- Thermal Energy: Due to temperature (random motion of particles).
- Electrical Energy: Due to electric charges.
Illustrative Image
Summary Table
| Type of Energy | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Kinetic Energy | KE = (1/2)mv² | Moving car |
| Potential Energy | PE = mgh | Stone at height |
| Mechanical Energy | KE + PE | Swinging pendulum |



Just a smiling visitant here to share the love (:, btw great design.