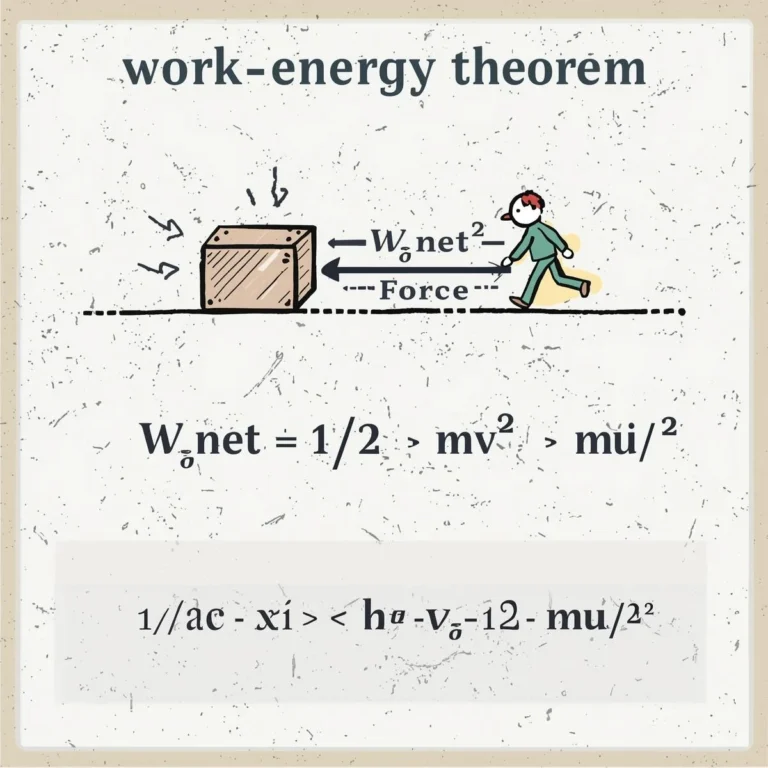
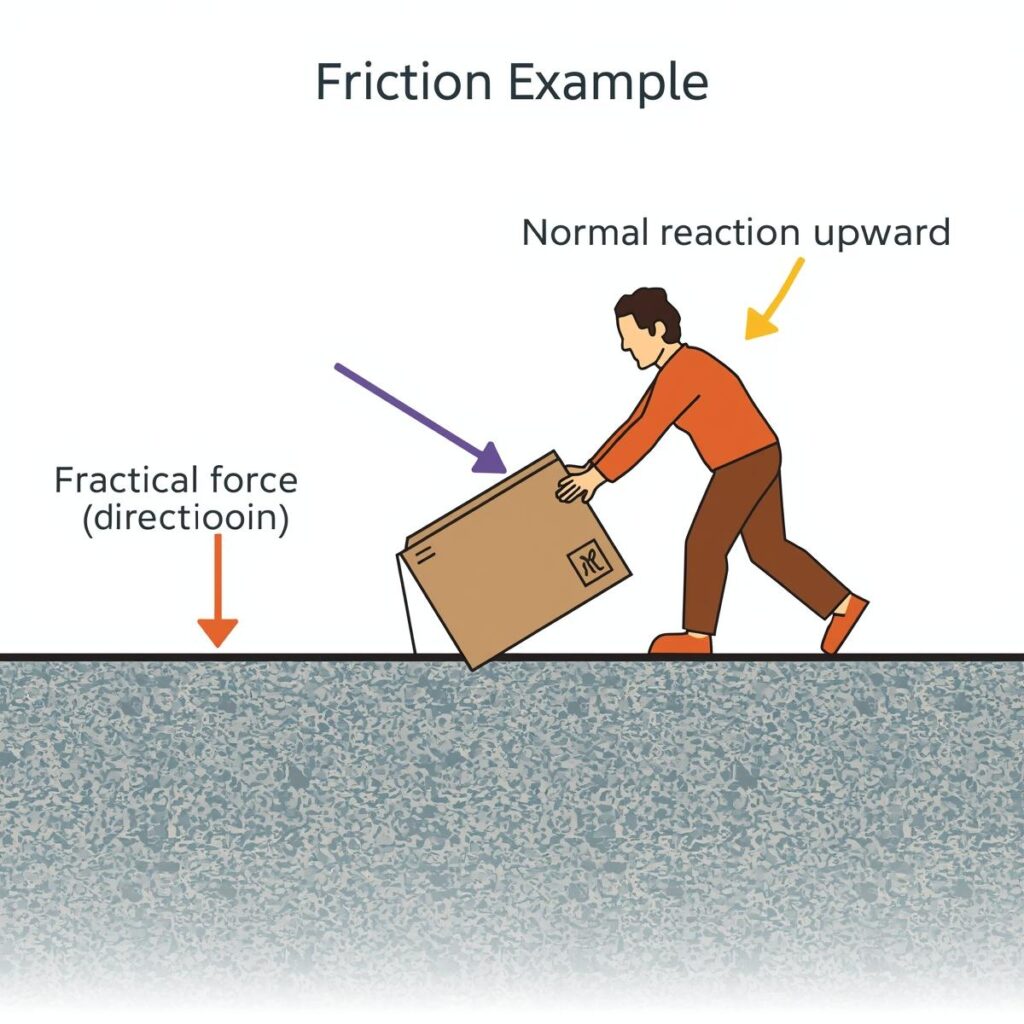
Definition
Friction is the force that opposes the relative motion or tendency of such motion of two surfaces in contact. It acts parallel to the surfaces and opposite to the direction of motion or attempted motion.
Types of Friction
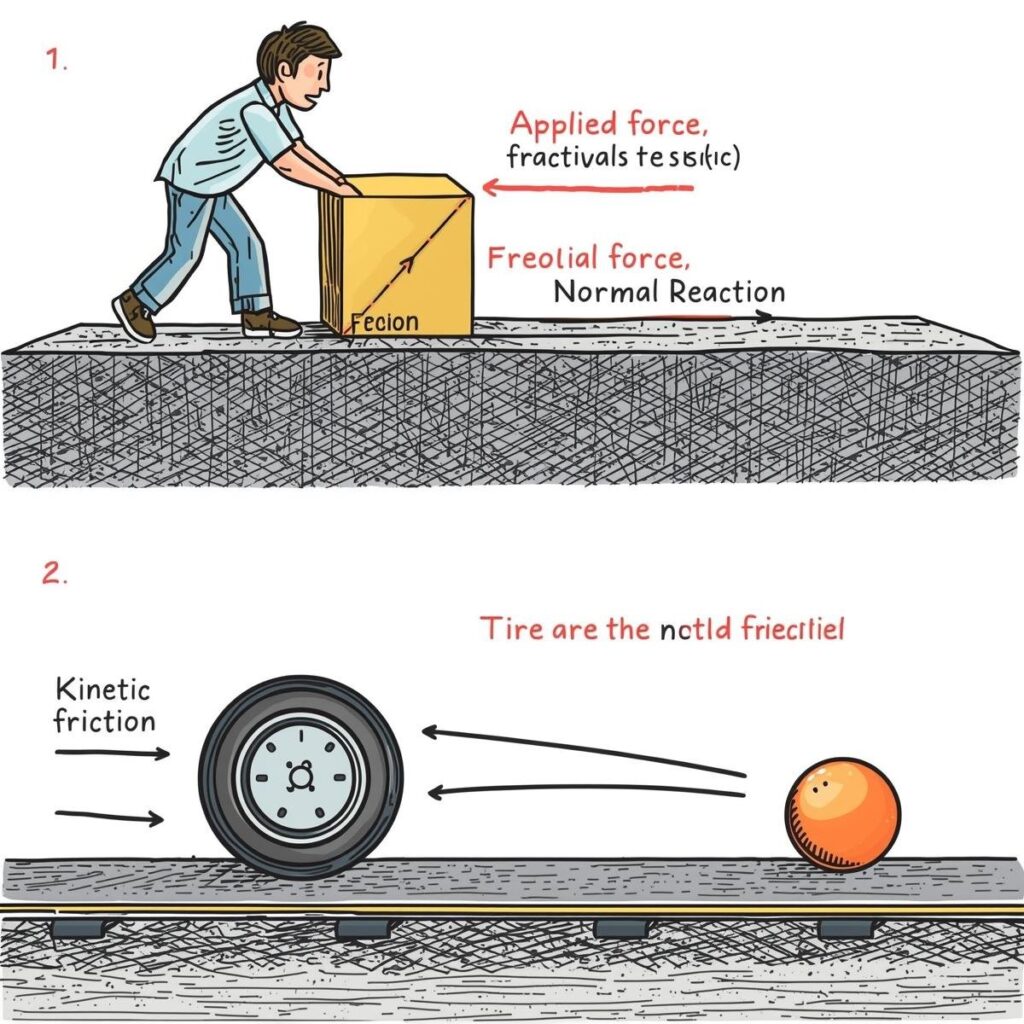
- Static Friction:
The frictional force that prevents two surfaces from sliding past each other. - Kinetic (Sliding) Friction:
The frictional force acting when two surfaces are sliding over each other. - Rolling Friction:
The frictional force when an object rolls over a surface.
Formulas
- Frictional Force (f):
f = μN
Where:- f = frictional force
- μ = coefficient of friction (dimensionless)
- N = normal reaction force (N)
- Limiting (Maximum Static) Friction:
fₛ(max) = μₛN
Where:- μₛ = coefficient of static friction
- Kinetic Friction:
fₖ = μₖN
Where:- μₖ = coefficient of kinetic friction
Example
A box of mass 5 kg rests on a horizontal surface. If the coefficient of static friction between the box and the surface is 0.4, the maximum static friction is:
fₛ(max) = μₛN = 0.4 × (5 × 9.8) = 0.4 × 49 = 19.6 N
Illustrative Image
Summary Table
| Type | Definition | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Static | Prevents motion | fₛ ≤ μₛN | Box at rest |
| Kinetic | Opposes sliding | fₖ = μₖN | Box sliding |
| Rolling | Opposes rolling | Usually < sliding friction | Ball rolling |