Impulse
Definition:
Impulse is the product of the average force applied to an object and the time interval over which it acts. It measures the effect of a force acting over time.
Formula:
Impulse (J) = F × Δt
Where:
- J = impulse (N·s or kg·m/s)
- F = average force (N)
- Δt = time interval (s)
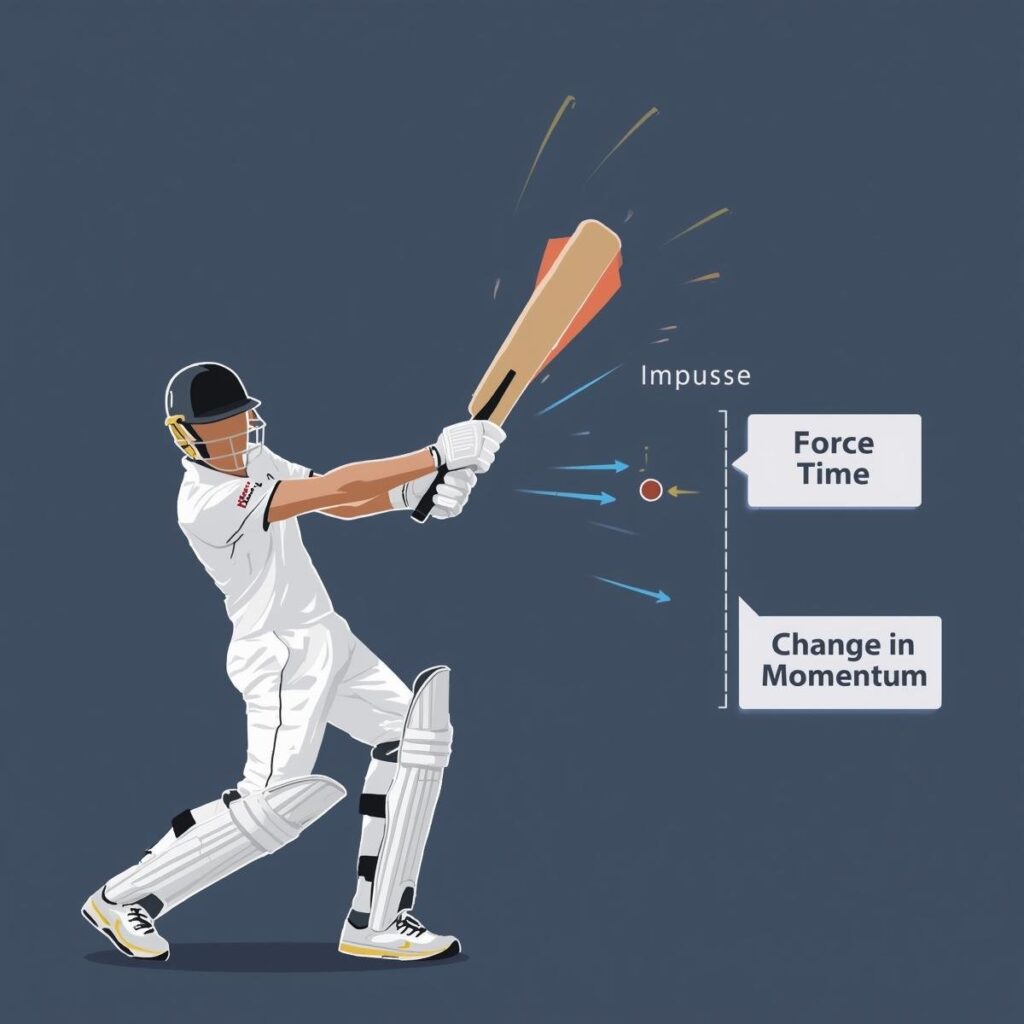
Example:
If a force of 10 N acts on a ball for 0.2 seconds:
J = 10 × 0.2 = 2 N·s
Impulse-Momentum Theorem
Definition:
The impulse experienced by an object is equal to the change in its momentum.
Formula:
Impulse (J) = Δp = m(v – u)
Where:
- Δp = change in momentum
- m = mass (kg)
- u = initial velocity (m/s)
- v = final velocity (m/s)
Example:
A 2 kg ball initially at rest (u = 0) is struck so it moves at 5 m/s (v = 5):
J = 2 × (5 – 0) = 10 N·s
Illustrative Image
Summary Table
| Concept | Definition | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Impulse | Effect of force over time | J = F × Δt | 10 N for 0.2 s: J = 2 N·s |
| Impulse-Momentum Theorem | Impulse equals change in momentum | J = m(v – u) | 2 kg ball, 0 to 5 m/s: J = 10 N·s |



This is going to be incredibly useful for my work.