Definition
A matrix is a rectangular arrangement of numbers, symbols, or expressions in rows and columns. The numbers or symbols in a matrix are called its elements or entries. If a matrix has m rows and n columns, it is called an m × n (read as “m by n”) matrix.
Types of Matrices
- Row Matrix: A matrix with only one row.
- Column Matrix: A matrix with only one column.
- Square Matrix: Number of rows = number of columns (m = n).
- Diagonal Matrix: A square matrix with all non-diagonal elements zero.
- Scalar Matrix: A diagonal matrix with all diagonal elements equal.
- Identity Matrix: A diagonal matrix with all diagonal elements equal to 1.
- Zero Matrix: All elements are zero.
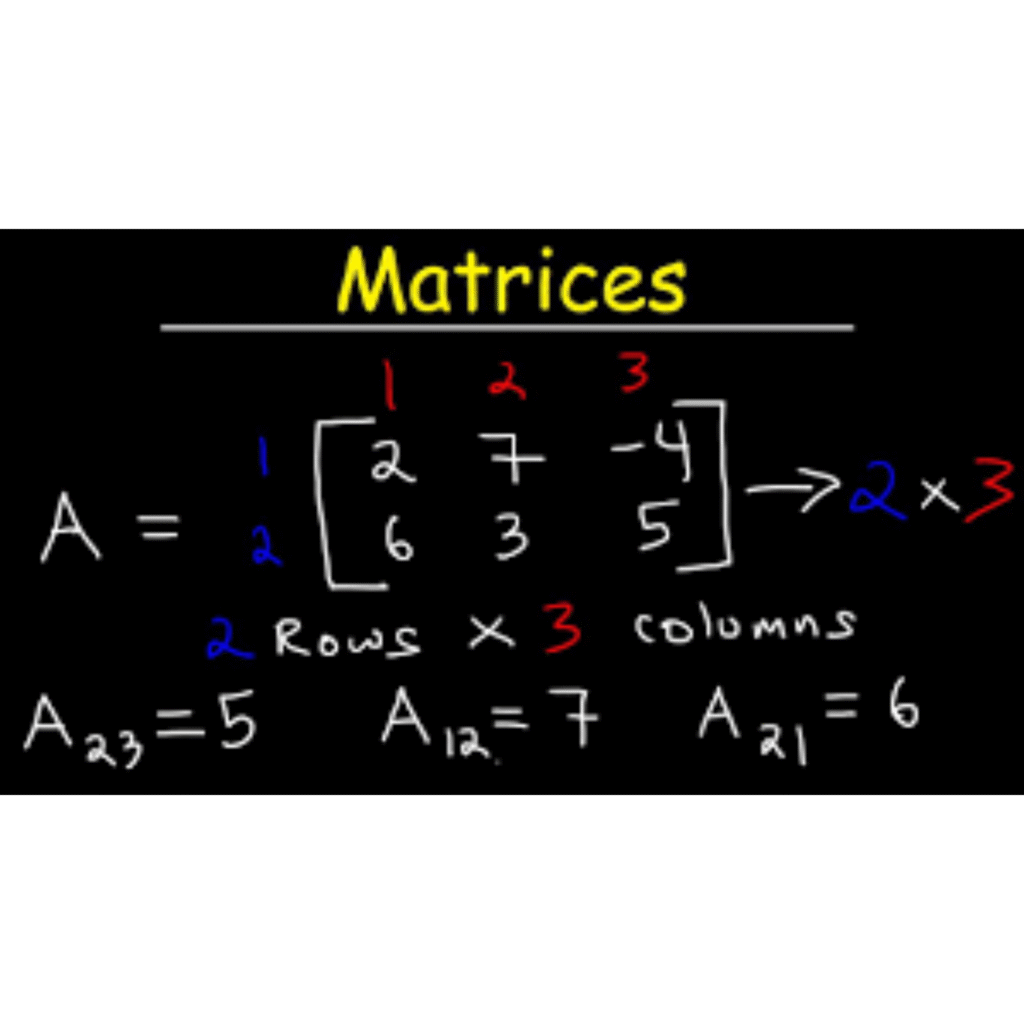
Example
Let
A = (\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 3 \ 4 & 5 \end{bmatrix})
This is a 2 × 2 matrix.
Matrix Notation
A matrix is usually denoted by a capital letter (A, B, C, etc.). The element in the i-th row and j-th column is denoted by (a_{ij}).
Basic Operations
1. Addition and Subtraction
If A and B are matrices of the same order, then
A + B = [a_{ij} + b_{ij}]
A – B = [a_{ij} – b_{ij}]
2. Scalar Multiplication
If k is a scalar and A = [a_{ij}], then
kA = [k × a_{ij}]
3. Matrix Multiplication
If A is an m × n matrix and B is an n × p matrix, then their product AB is an m × p matrix.
(AB){ij} = Σ (a{ik} × b_{kj}) for k = 1 to n
4. Transpose
The transpose of matrix A, denoted by A^T, is obtained by interchanging rows and columns.
If A = [a_{ij}], then A^T = [a_{ji}]
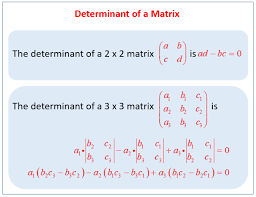
5. Determinant (for 2 × 2 matrix)
If A = (\begin{bmatrix} a & b \ c & d \end{bmatrix}),
then |A| = ad – bc
6. Inverse (for 2 × 2 matrix)
If A = (\begin{bmatrix} a & b \ c & d \end{bmatrix}),
and |A| ≠ 0, then
A^{-1} = (1/|A|) × (\begin{bmatrix} d & -b \ -c & a \end{bmatrix})
Example Calculations
Let
A = (\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 2 \ 3 & 4 \end{bmatrix}),
B = (\begin{bmatrix} 5 & 6 \ 7 & 8 \end{bmatrix})
- Addition:
A + B = (\begin{bmatrix} 1+5 & 2+6 \ 3+7 & 4+8 \end{bmatrix}) = (\begin{bmatrix} 6 & 8 \ 10 & 12 \end{bmatrix}) - Scalar Multiplication:
2A = (\begin{bmatrix} 2×1 & 2×2 \ 2×3 & 2×4 \end{bmatrix}) = (\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 4 \ 6 & 8 \end{bmatrix}) - Matrix Multiplication:
AB = (\begin{bmatrix} (1×5+2×7) & (1×6+2×8) \ (3×5+4×7) & (3×6+4×8) \end{bmatrix})
= (\begin{bmatrix} 19 & 22 \ 43 & 50 \end{bmatrix}) - Transpose:
A^T = (\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 3 \ 2 & 4 \end{bmatrix}) - Determinant:
|A| = (1×4) – (2×3) = 4 – 6 = -2 - Inverse:
A^{-1} = (1/(-2)) × (\begin{bmatrix} 4 & -2 \ -3 & 1 \end{bmatrix})
= (\begin{bmatrix} -2 & 1 \ 1.5 & -0.5 \end{bmatrix})
Summary Table
| Operation | Formula/Result |
|---|---|
| Addition | A + B = [a_{ij} + b_{ij}] |
| Scalar Multiplication | kA = [k × a_{ij}] |
| Matrix Multiplication | (AB){ij} = Σ (a{ik} × b_{kj}) |
| Transpose | A^T = [a_{ji}] |
| Determinant (2×2) | ad – bc |