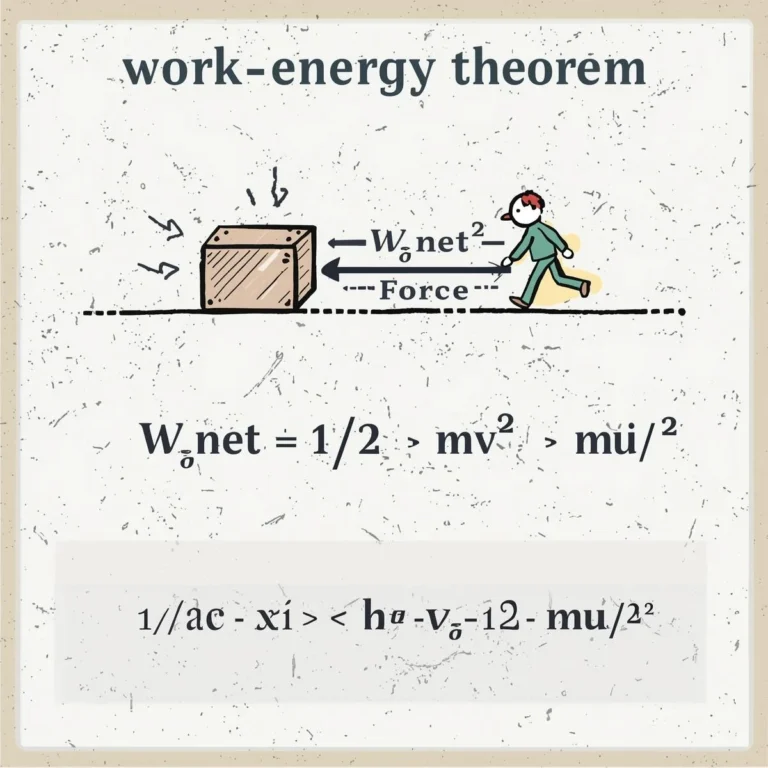
Momentum
Definition:
Momentum is the quantity of motion possessed by a moving body. It is the product of the mass and velocity of the object.
Formula:
p = m × v
Where:
- p = momentum (kg·m/s)
- m = mass (kg)
- v = velocity (m/s)
Example:
A cricket ball of mass 0.15 kg moving with a velocity of 20 m/s has a momentum:
p = 0.15 × 20 = 3 kg·m/s
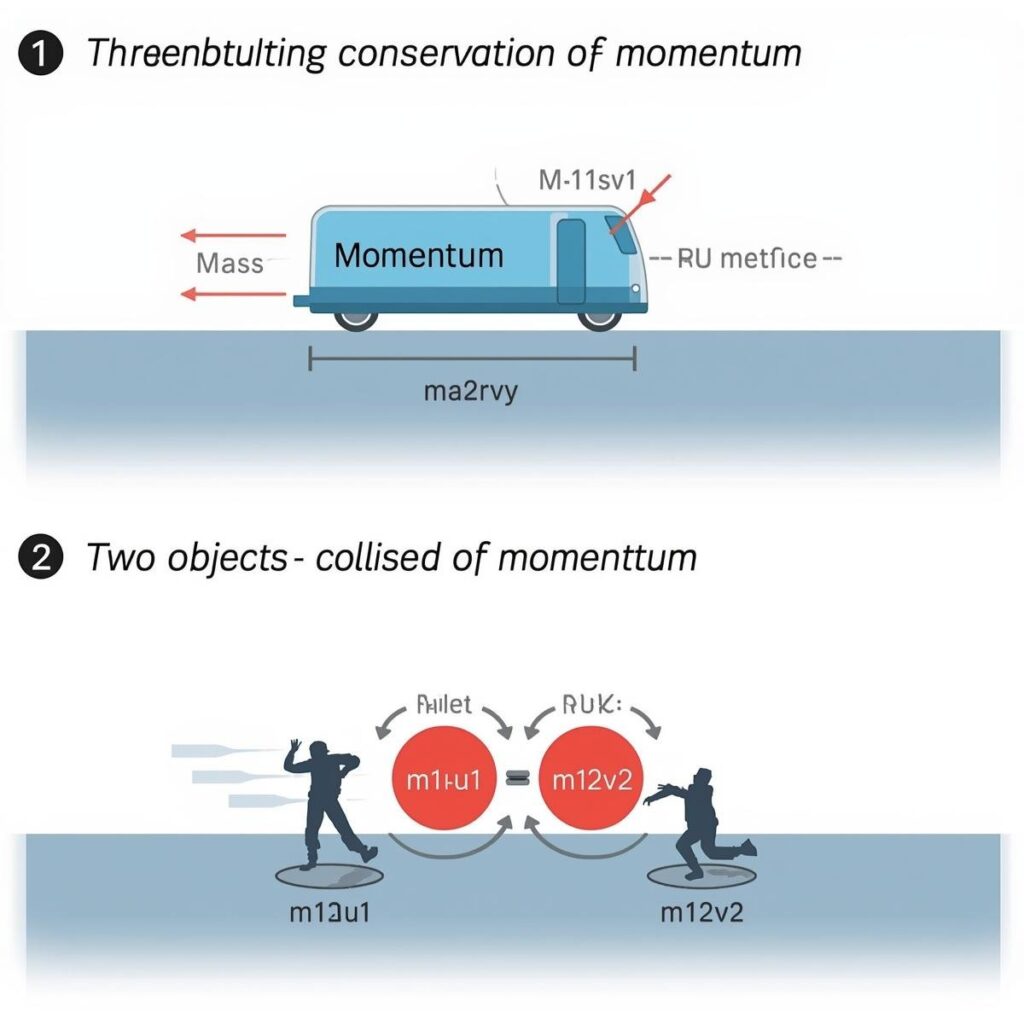
Law of Conservation of Momentum
Definition:
When two or more bodies act upon one another, their total momentum remains constant, provided no external force acts on them.
Formula:
m₁u₁ + m₂u₂ = m₁v₁ + m₂v₂
Where:
- m₁, m₂ = masses of two objects
- u₁, u₂ = initial velocities
- v₁, v₂ = final velocities
Example:
If two ice skaters push off from each other, the total momentum before and after pushing remains the same, assuming no external force.
Illustrative Image
Summary Table
| Concept | Definition | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Momentum | Quantity of motion of a body | p = m × v | Cricket ball: 0.15 kg × 20 m/s = 3 kg·m/s |
| Conservation of Momentum | Total momentum remains constant in absence of external force | m₁u₁ + m₂u₂ = m₁v₁ + m₂v₂ | Two skaters pushing off |